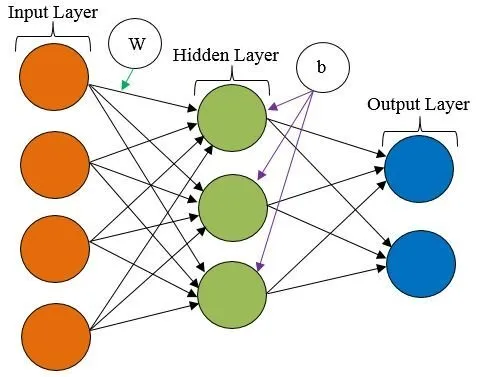
Artificial neural networks are comprised of node layers containing
an input layer, one or more hidden layers, and an output layer. Each
node connects to another and has an associated weight and threshold
value.
For generating random colored images we will develop an ANN
architecture that takes each pixel value as an input. All inputs are
modified by weight and summed. For handling the n-dimensional data
as an input we can use the techniques mentioned below.
Techniques used
- NumPy
- Statistics
- Activation functions
- OpenCV
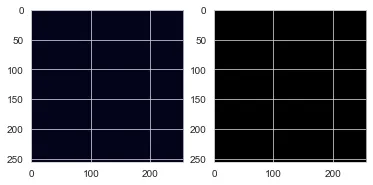
Selecting the size of an image as an input in the form of height and
weight ex: image width = 216 and image height = 216 which gives us a
black image.
Once we are representing a greyscale image it becomes and 2-d array
format data. But when we are using a colored image 3-d array format
data will be created.
For generating the random images we need to convert the 2-d image
greyscale data into the 3-d format. We can collect every pixel on
the x and y-axis and copy them in 3-dimensional formats. This
converts 2-d data into 3-d data and we need to specify which color
mode to use and whether to use the Alpha channel or not.

Neural Network Architecture
For creating a Neural Network we need to define input data, Hidden
layers, and the number of neurons per layer, and the Activation
Function.
Suppose we have (512,512) images. what neural network does is will
collect every pixel value fun{i,j} to computer r,g,b,a values.
So total we are having 5 input dimension data. Each pixel converts
into 5 different values to generate r,g,b, a, and bias values.
Value = min(image height and image width)
Input1 = i / value – 0.5
Input2 = j / value – 0.5
Z = sqt(input1 + input2)
Z1 = random value from -1 to 1 Alpha
Z2 = random value from -1 to 1 Bias
These input values were added with some random weights along with
the activation function for each neuron. On selecting the color mode
the values get changes for the output layer.
Activation Functions used
- Sigmoid
- relu
- Softmax
- Tanh
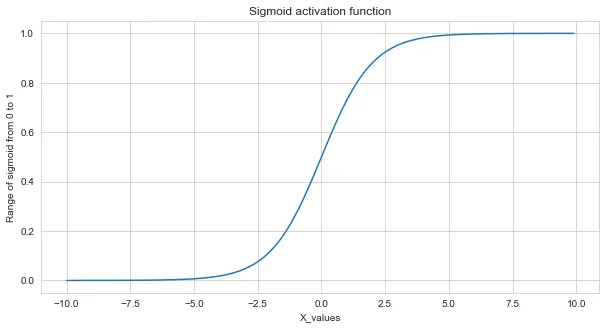
Sigmoid Activation Function
Sigmoid activation function range is from 0 to 1 and their
derivative range is from 0 to 0.25 so there is a vanishing gradient
problem if we use the sigmoid activation function in the hidden
layers.
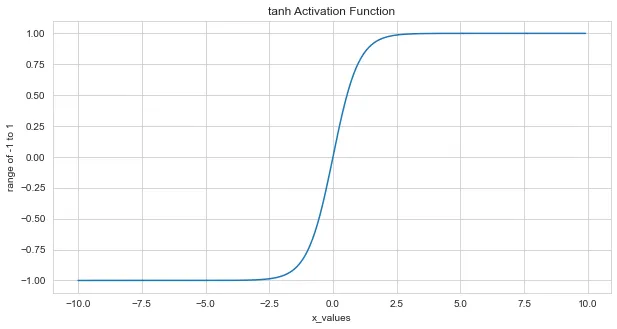
Tanh Activation Function
Tanh activation function range is from -1 to 1 . since the range is
quite high we can overcome the vanishing gradient problem if we need
to update the weights using backpropagation.
Selecting Color Mode
The output layers depend on which color mode we select. Using RGB,
CMYK, and HSV, and HSL we generated our images. If we are not using
any color mode just the input data were gone through a neural
network and gives 3 output layers for R, G, B channels. But if we
use color mode each pixel again goes under their own maths
calculation for changing the values.
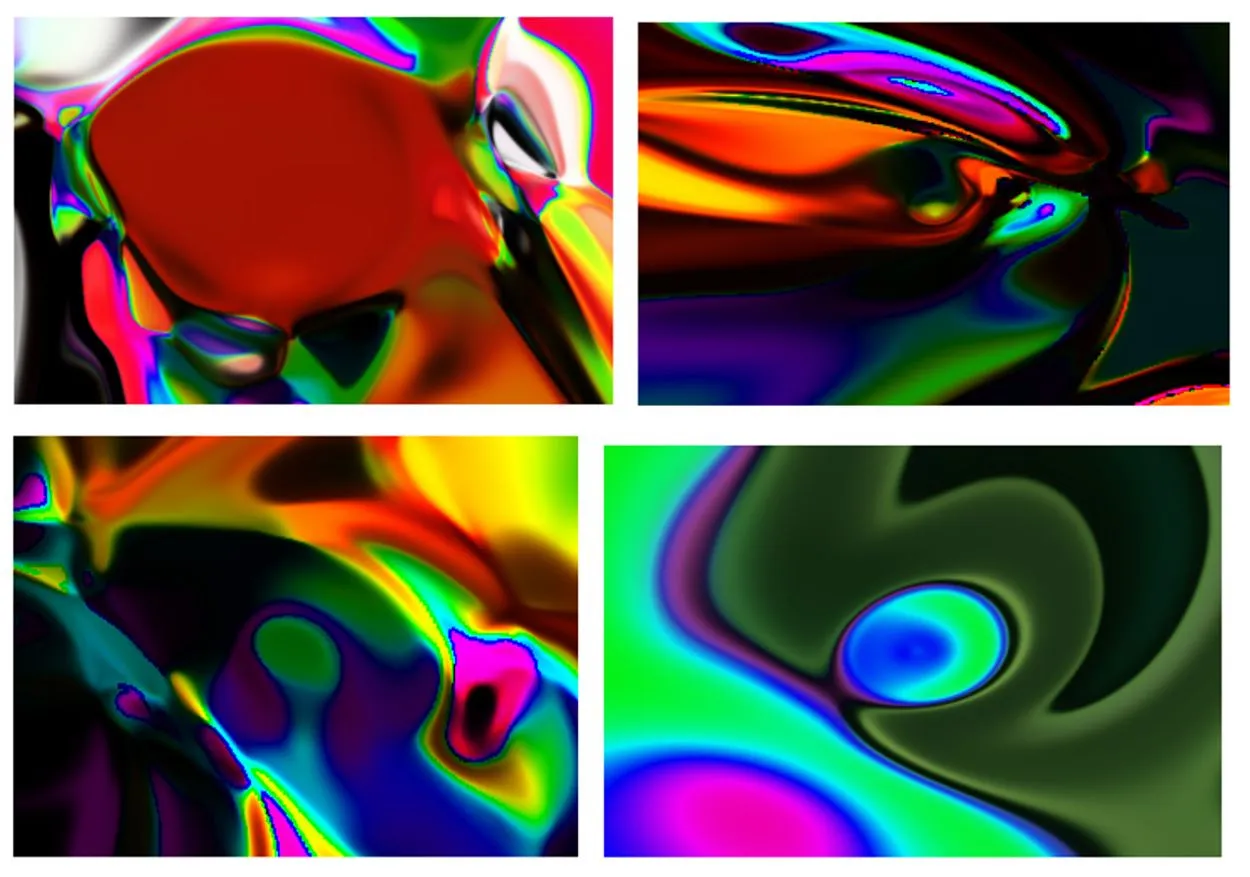
Some images generated with RGB color mode
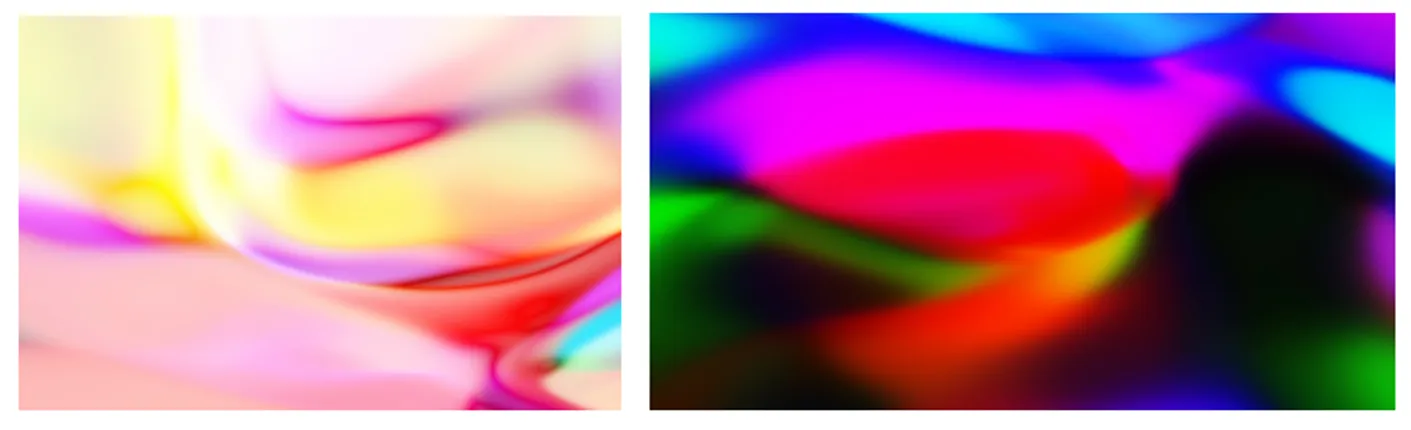
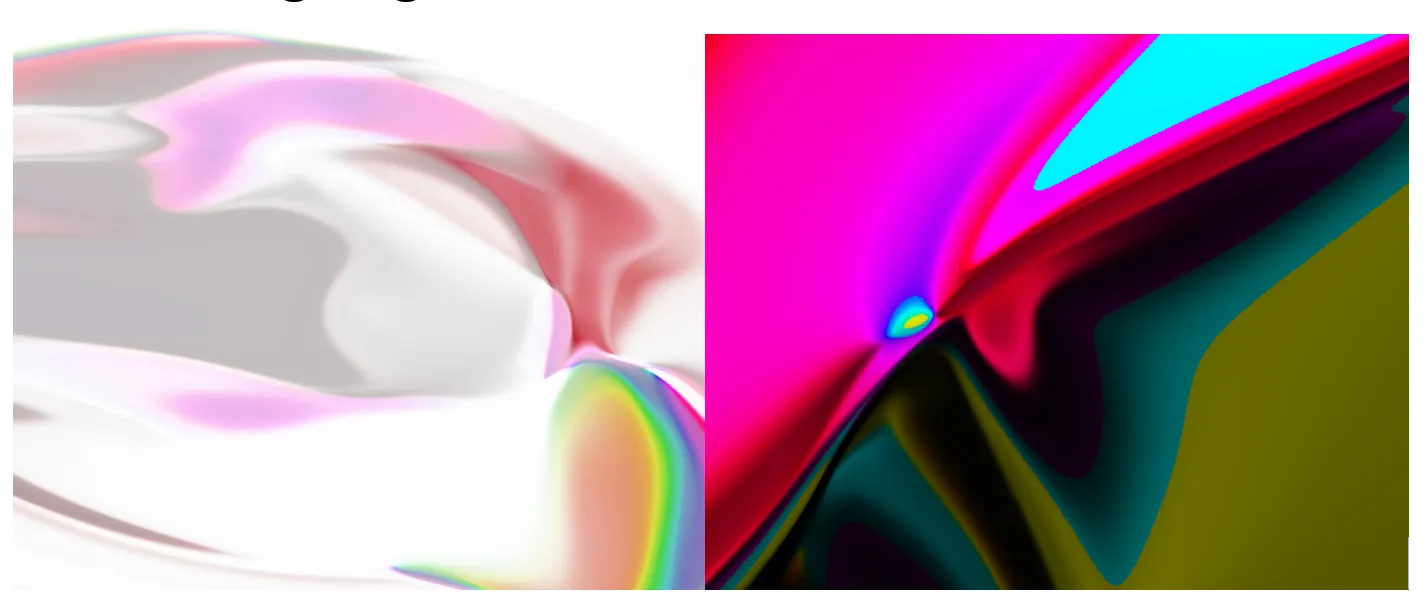
Some images generated with HSV and HSL color Mode

For removing the noise and to make the images more sharpened we need
to add some kernel values on the top of the image, this can easily
be done by the OpenCV framework. Some random kernel values (3*3)
were placed on the top of the generated image.
Converting input values into specified color mode
Changing input data into CMYK format by adding their input weights
The R, G, B values are divided by 255 to change the range from 0 to
1.
R = R / 255 , G = G / 255 , B = B / 255
Value k can be calculated from RGB k = 1 – max(R,G,B)
The cyan color will be calculated from red and k[black] c = (1-R-K)
/ (1-K)
The Magenta color will be calculated from green and black m =
(1-G-K) / (1-K)
The yellow color will be calculated from blue and black y = (1-B-K)
/ (1 – K)
Some images were generated using CMYK color mode