Welcome to this exploration of Advanced SQL - Window FunctionsPart 3.
** To learn frame type - ROWS, RANGE, and GROUPS, refer to the part 1 of this blog series
** To Discover more about EXCLUDE, PARTITION BY, LAG and LEAD, refer to the part 2 of this blog series
RECAP:
What are window functions?
With SQL:2003, the ISO SQL Standard introduced window functions, a new mode of row-based computation:
Input Output
Aggregate functions(sum, avg, count) group of rows → row (one per group)
window function row vicinity → row (one per row)
- Window functions operate on a set of rows ( commonly known as window or frame or row vicinity) and return a single value for each row.
- The term window describes the set of rows on which the function operates.
- A window function uses values from the rows in a window.
In the Part 1 of this blog series, we learnt how to create a frame using frame_types - ROWS, RANGE and GROUPS.
In the part 2 of this blog series, we learnt about different functions like EXCLUDE, PARTITION BY, LAG and LEAD
Now we'll see more about the other functionality that window functions provide.
1. FIRST_VALUE, LAST_VALUE, NTH_VALUE
Aggregates reduce all rows inside a frame to a single value.
Now for something different:
Positional access to individual rows inside a frame is
provided by three window functions:
FIRST_VALUE(e)
LAST_VALUE(e)
NTH_VALUE(e,n)
NTH_VALUE(A,s): will return
NULL if the index is not present
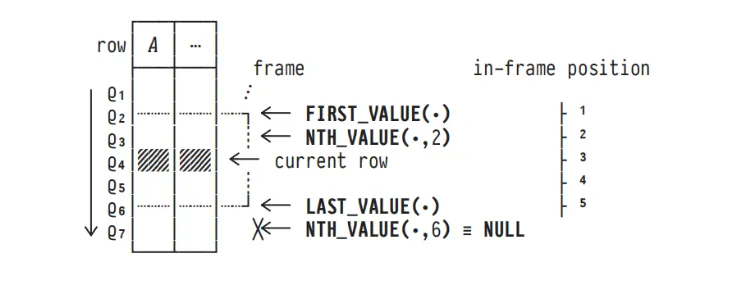
NOTE: FIRST_VALUE(e) ≡ NTH_VALUE(e,1).
Query 1 : FIRST_VALUE, LAST_VALUE, NTH_VALUE example
SELECT w."row" AS "current row",
array_agg(w."row") OVER win AS "rows in frame",
FIRST_VALUE(w."row") OVER win AS "first row",
LAST_VALUE(w."row") OVER win AS "last row",
NTH_VALUE(w."row",2) OVER win AS "second row"
FROM sample AS w
WINDOW win AS (ORDER BY w.a ROWS BETWEEN 2 PRECEDING AND 2 FOLLOWING)
ORDER BY w.a, w.row;
OUTPUT -
current row | rows in frame | first row | last row | second row
------------+---------------------+-----------+----------+------------
Q1 | {Q1,Q2,Q3} | Q1 | Q3 | Q2
Q2 | {Q1,Q2,Q3,Q4} | Q1 | Q4 | Q2
Q3 | {Q1,Q2,Q3,Q4,Q5} | Q1 | Q5 | Q2
Q4 | {Q2,Q3,Q4,Q5,Q6} | Q2 | Q6 | Q3
Q5 | {Q3,Q4,Q5,Q6,Q7} | Q3 | Q7 | Q4
Q6 | {Q4,Q5,Q6,Q7,Q8} | Q4 | Q8 | Q5
Q7 | {Q5,Q6,Q7,Q8,Q9} | Q5 | Q9 | Q6
Q8 | {Q6,Q7,Q8,Q9} | Q6 | Q9 | Q7
Q9 | {Q7,Q8,Q9} | Q7 | Q9 | Q8
Explanation -
For the current row Q4
Frame type - ROWS
Window - ROWS BETWEEN 2PRECEDING AND 2 FOLLOWING -
{Q2,Q3,Q4,Q5,Q6}
Q2 and Q3 are 2 preceding, Q5 and Q6 are 2 following
FIRST_VALUE = Q2 as that is the first element in the window
LAST_VALUE = Q6 as that is the last element in the window
NTH_VALUE(w.row, 2) - Q3 as it as the 2nd index
Django Query 1 : FIRST_VALUE, LAST_VALUE, NTH_VALUE example
from django.db.models import Avg, F, RowRange, Window, Count, Sum
from django.db.models.functions import Lag, Lead, LastValue, NthValue, FirstValue
window = {
'frame': RowRange(start=-2, end=2),
'order_by': F('a').asc()
}
qs = Sample.objects.annotate(
first = Window(
expression=FirstValue('row'), **window
),
last = Window(
expression=LastValue('row'), **window
),
second_val = Window(
expression=NthValue('row', 2), **window
),
).order_by('a')
for i in qs:
print(i.row, i.a, i.b, i.first, i.last, i.second_val)
OUTPUT -
Q1 1 False Q1 Q3 Q2
Q2 2 True Q1 Q4 Q2
Q3 3 True Q1 Q5 Q2
Q4 3 False Q2 Q6 Q3
Q5 3 True Q3 Q7 Q4
Q6 4 True Q4 Q8 Q5
Q7 6 False Q5 Q9 Q6
Q8 6 False Q6 Q9 Q7
Q9 7 True Q7 Q9 Q8
2. ROW_NUMBER(), DENSE_RANK(), RANK()
Countless problem scenarios involve the number (position) or
rank of the current row in an ordered sequence of rows.
Family of window functions to number/rank rows:
ROW_NUMBER()
DENSE_RANK()
RANK()
Scope is the partition (if present)—FRAME
is irrelevant.
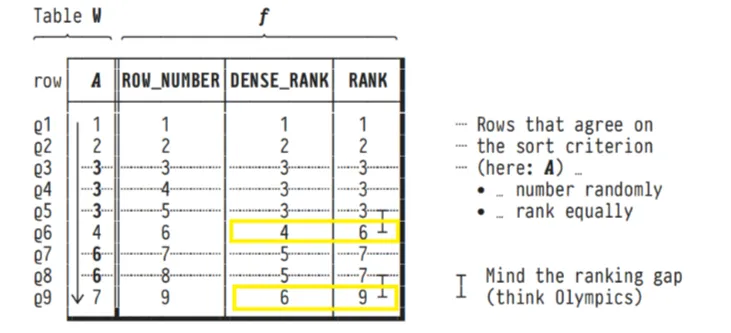
ROW_NUMBER - gives incremental row number to all the rows
DENSE_RANK - Peer rows (rows with same values) will share a
common rank. No rank numbers are lost.
RANK - Peer rows (rows with same values) will share a common
rank. In this case rank numbers are lost.
Query 2 : ROW_NUMBER, DENSE_RANK, RANK example
SELECT w."row" AS "current row",
w.a,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER win AS "ROW_NUMBER",
DENSE_RANK() OVER win AS "DENSE_RANK",
RANK() OVER win AS "RANK"
FROM sample AS w
WINDOW win AS (ORDER BY w.a)
ORDER BY w.a;
OUTPUT -
current row | a | ROW_NUMBER | DENSE_RANK | RANK
------------+---+------------+------------+------
Q1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1
Q2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2
Q3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3
Q4 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 3
Q5 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 3
Q6 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 6
Q7 | 6 | 7 | 5 | 7
Q8 | 6 | 8 | 5 | 7
Q9 | 7 | 9 | 6 | 9
Django Query 2 : ROW_NUMBER, DENSE_RANK, RANK example
from django.db.models import Avg, F, RowRange, Window, Count, Sum
from django.db.models.functions import Lag, Lead, DenseRank, Rank, RowNumber
window = {
'order_by': F('a').asc()
}
qs = Sample.objects.annotate(
row_number = Window(
expression=RowNumber(), **window
),
rank = Window(
expression=Rank(), **window
),
dense_rank = Window(
expression=DenseRank(), **window
),
).order_by('a')
for i in qs:
print(i.row, i.a, i.b, i.row_number, i.dense_rank, i.rank)
OUTPUT -
Q1 1 False 1 1 1
Q2 2 True 2 2 2
Q3 3 True 3 3 3
Q4 3 False 4 3 3
Q5 3 True 5 3 3
Q6 4 True 6 4 6
Q7 6 False 7 5 7
Q8 6 False 8 5 7
Q9 7 True 9 6 9
3. NTILE
NTILE creates equal chunks or partitions of data.
Example if NTILE(3) is specified, then chunks of 3 records are
created.
Query 3 : NTILE example
SELECT w."row" AS "current row",
w.a,
NTILE(3) OVER win AS "NTILE(3)"
FROM sample AS w
WINDOW win AS (ORDER BY w.a)
ORDER BY w.a;
OUTPUT -
current row | a | NTILE(3)
------------+---+----------
Q1 | 1 | 1
Q2 | 2 | 1
Q3 | 3 | 1
Q4 | 3 | 2
Q5 | 3 | 2
Q6 | 4 | 2
Q7 | 6 | 3
Q8 | 6 | 3
Q9 | 7 | 3
Django Query 3 : NTILE example
from django.db.models.functions import Ntile
window = {
'order_by': F('a').asc()
}
qs = Sample.objects.annotate(
ntile = Window(
expression=Ntile(3), **window
),
).order_by('a')
for i in qs:
print(i.row, i.a, i.b, i.ntile)
OUTPUT -
Q1 1 False 1
Q2 2 True 1
Q3 3 True 1
Q4 3 False 2
Q5 3 True 2
Q6 4 True 2
Q7 6 False 3
Q8 6 False 3
Q9 7 True 3
This is not the end of window functions. We will use all the
knowledge gained till now and solve problems in the next part of
this window function blog series.
… to be continued